备注:第33课已经OK
一、urllib
1 | from urllib.request import urlopen as uReq |
2 | from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as soup |
5 | # opening up connection, grabbing the page |
7 | page_html = uClient.read() |
9 | page_soup = soup(page_html,"html.parser") |
二、异常处理
使用下面的方法打印出错信息:
7 | # print("error message") |
try的工作原理是,当开始一个try语句后,python就在当前程序的上下文中作标记,这样当异常出现时就可以回到这里,try子句先执行,接下来会发生什么依赖于执行时是否出现异常。
如果当try后的语句执行时发生异常,python就跳回到try并执行第一个匹配该异常的except子句,异常处理完毕,控制流就通过整个try语句(除非在处理异常时又引发新的异常)。
如果在try后的语句里发生了异常,却没有匹配的except子句,异常将被递交到上层的try,或者到程序的最上层(这样将结束程序,并打印缺省的出错信息)。
如果在try子句执行时没有发生异常,python将执行else语句后的语句(如果有else的话),然后控制流通过整个try语句。
三、读取CSV文件到SQlite
3 | conn= sqlite3.connect("dbname.db") |
4 | df = pandas.read_csv('btc2017_new2.csv') |
5 | df.to_sql('tablename', conn, if_exists='append', index=False) |
四、读取txt
2 | f = open("guessword.txt") |
3 | words = f.read().splitlines() |
6 | print("Cannot find the 'gusssword.txt'") |
五、读取文件夹下面的文件(使用glob)
2 | files = glob.glob("*.nille") |
4 | print(str(filesIndex) + "."+ filename) |
5 | filesIndex = filesIndex + 1 |
六、函数内部调用自己
8 | timer = threading.Timer(5.8,fun_timer) |
11 | timer = threading.Timer(2,fun_timer) |
另一个:
1 | from threading import Timer |
4 | Timer(2.0, hello) .start() |
另一个:定时器:
threading中定时器Timer
定时器功能:在设置的多少时间后执行任务,不影响当前任务的执行。
2 | from datetime import datetime |
6 | print("hello timer!===处理每秒触发的计时器事件:%s"% str(datetime.now())) |
8 | global timer #timer可以改为其它名称 |
10 | timer = threading.Timer(2, fun_timer) |
执行结果:
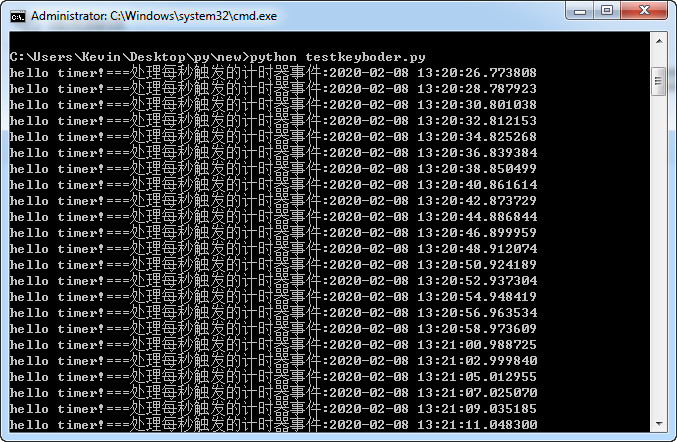
七、导入相同目录下的其他python文件
命令式编程关键字: def if else for
函数式编程:关键字 map reduce filter三个函数,lambda算子
八、列表中的数值求和
1 | from functools import reduce |
3 | list_x = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] |
5 | r = reduce(lambda x,y:x+y,list_x) |
结果为36
九、filter
1 | from functools import reduce |
3 | list_x = [1,0,1,0,5,0,7,8] |
5 | r = filter(lambda x: True if x ==1 else False,list_x) |
结果为[1, 1]
可以简写为:r = filter(lambda x: x,list_x)
十、装饰器
5 | print("This is a function") |
如果要给上面一百个函数添加时间的功能呢?
5 | print("This is a function") |
10 | def print_current_time(func): |
要懂装饰器首先要懂闭包,最好的视频还是这个:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1k7411i7oy?p=242
十一、叠代器
叠代器的优点就是占用很小的空间,它存储的不是数据,而是产生数据的方法。
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Fb411L7d8/?spm_id_from=autoNext
之前没懂,看完下面这个例子终于懂了:
2 | """什么样的对象对能被iterater?只要将下面两个方法定义好就可以了,就可以被for循化""" |
10 | self.a, self.b = self.b, self.a + self.b |
这个视频解释得很好:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av50369911/
十二、生成器
是一种特殊的迭代器。
将推导列表的方括号变成圆括号,就是生成器。用yield。
g= (x** for x in range(10))
3 | def fibonacci(n): # 生成器函数 - 斐波那契 |
4 | a, b, counter = 0, 1, 0 |
11 | f = fibonacci(10) # f 是一个迭代器,由生成器返回生成 |
15 | print (next(f), end=" ") |
结果:
“0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55”
十三、闭包
看了很多说明,还是没有说明白的,后来看了这个视频懂了:闭包就是外面的函数返回里面的函数的地址。
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1k7411i7oy?p=240
十三、其他
1.列表生成式
[stock for stock in tohold if stock not in context.portfolio.positions ]
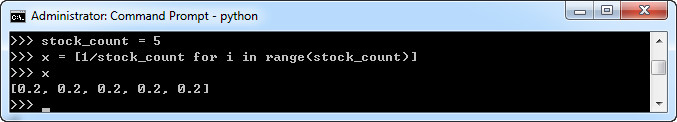
十四、股票权重生成器
十五、处理时间格式
将“201902251030”的时间格式转化为“2010-02-25 10:30”的形式
1 | =df['candel_end_time'].apply(lambda x: '%s-%s-%s' %s:%s) % (x[0:4],x[4:6],x[6:8],x[8:10],x[10:12]) |
十六、sys.argv[0] 表示脚本名
3 | print '参数个数为:', len(sys.argv), '个参数。' |
4 | print '参数列表:', str(sys.argv) |
输出结果为:
1 | $ python test.py arg1 arg2 arg3 |
3 | 参数列表: ['test.py', 'arg1', 'arg2', 'arg3'] |
十七、 if写成一行,采集的时候,比如要写两个采集规则的时候可以使用。
执行结果为5。



